Page 35 - MOH Supply and Needs-Based Requirement Hyperlink 02032021
P. 35
27 EXTENDED EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.4.2 The Requirement Model
The Needs-based requirement model for each selected health profession was also developed
using the system dynamics approach. The requirement model was used to determine the
number of HRH workforce required to attain the population health care needs
(as opposed to health care demand/utilisation). The needs are derived from the
factors included in the Needs-based approach and defined from the perspective
of health care providers. In this study, however, the term health care ‘demand’ was
used in what-if scenario analysis to refer to the ‘adjusted need’ which is defined as
the health care needs adjusted to follow closely the current health care utilisation.
The requirement models for all professions were structured based on three (3) categories of
Malaysian common health care provider’s services which were the preventive care, disease-
based care, and other health care services. Each of these categories were further broken
down into relevant sub-categories, each to correspond to the requirement sub-models, as
detailed in Table 8, Table 9, Table 10, Table 11 and Table 12 for Doctor, Dentist, Pharmacist,
Nurse and AMO, respectively. Note that the requirement models for Pharmacist, Nurse and
AMO are heavily based on output from the Doctor’s requirement model. The sub-models
listed in table 4c, 4d and 4e are additional and specific to Pharmacist, Nurse and AMO.
Figures 10a, 10b and 10c are samples of SD-based requirement model for Doctor, Dentist,
Pharmacist, Nurse and AMO, respectively.
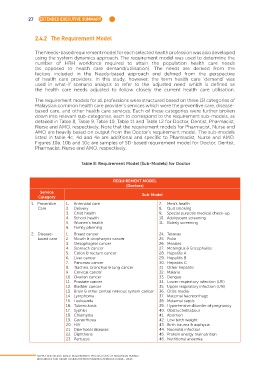
Table 8: Requirement Model (Sub-Models) for Doctor
REQUIREMENT MODEL
(Doctors)
Service Sub-Model
Category
1. Preventive 1. Antenatal care 7. Men’s health
Care 2. Delivery 8. Quit smoking
3. Child health 9. Special purpose medical check-up
4. School health 10. Adolescent screening
5. Women’s health 11. Elderly screening
6. Family planning
2. Disease- 1. Breast cancer 24. Tetanus
based care 2. Mouth & oropharynx cancer 25. Polio
3. Oesophageal cancer 26. Measles
4. Stomach cancer 27. Meningitis & Encephalitis
5. Colon & rectum cancer 28. Hepatitis A
6. Liver cancer 29. Hepatitis B
7. Pancreas cancer 30. Hepatitis C
8. Trachea, bronchus & lung cancer 31. Other hepatitis
9. Cervical cancer 32. Malaria
10. Ovarian cancer 33. Dengue
11. Prostate cancer 34. Lower respiratory infection (LRI)
12. Bladder cancer 35. Upper respiratory infection (URI)
13. Brain & other central nervous system cancer 36. Otitis media
14. Lymphoma 37. Maternal haemorrhage
15. Leukaemia 38. Maternal sepsis
16. Tuberculosis 39. Hypertensive disorder of pregnancy
17. Syphilis 40. Obstructed labour
18. Chlamydia 41. Abortion
19. Gonorrhoea 42. Low birth weight
20. HIV 43. Birth trauma & asphyxia
21. Diarrhoeal diseases 44. Neonatal infection
22. Diphtheria 45. Protein energy malnutrition
23. Pertussis 46. Nutritional anaemia
SUPPLY AND NEEDS-BASED REQUIREMENT PROJECTIONS OF MALAYSIAN HUMAN
RESOURCES FOR HEALTH USING SYSTEM DYNAMICS APPROACH 2016 - 2030